From Theory to Practice
Real-World Adaptive Radiotherapy
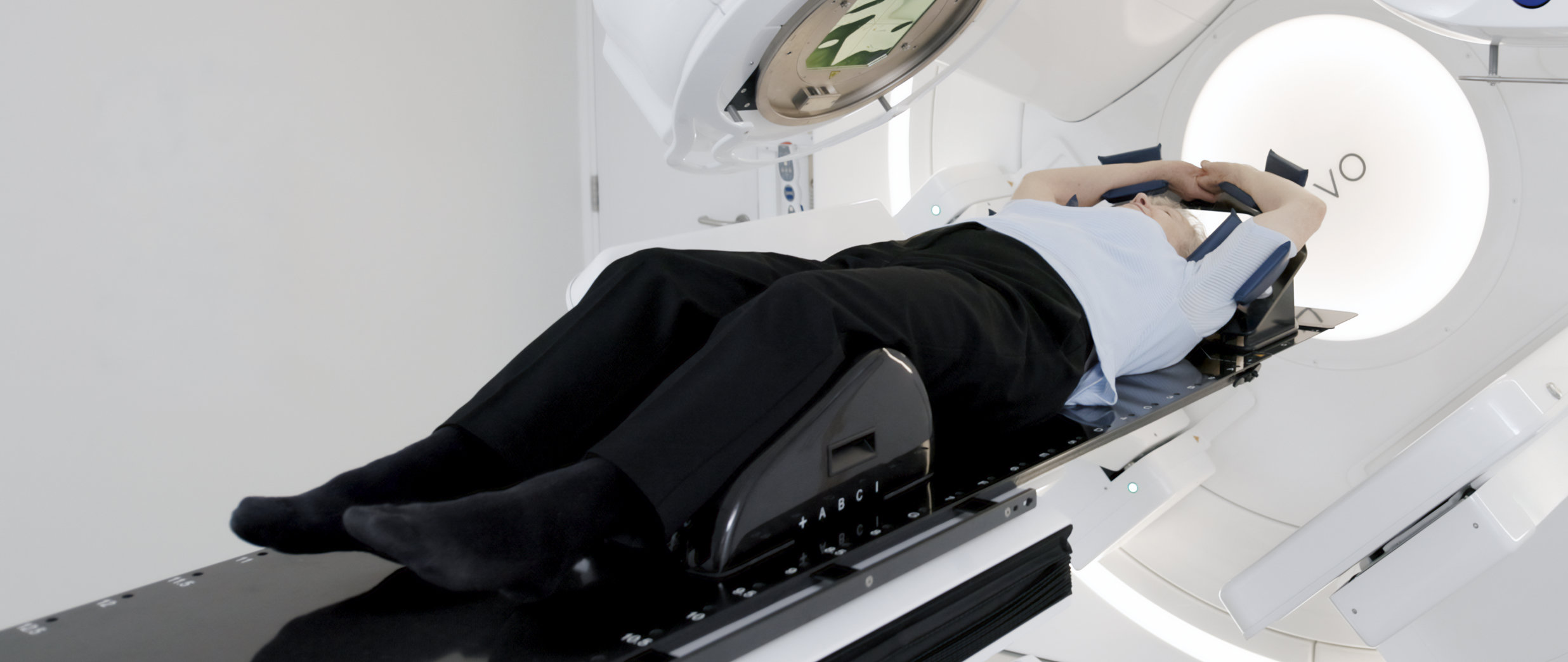
Innovations in CBCT and MRI technology, which are now increasingly combined with AI-based algorithms and automation, provide solutions in the form of Adaptive Radiotherapy. Today, a treatment plan is no longer a fixed roadmap, but rather a starting point that can be continuously adjusted to ensure precise targeting of the tumor as its size, shape, and relative position change throughout the course of therapy.
The ability to rapidly capture and analyze high-quality images allows treatment replanning every few sessions or even daily, depending on the tumor’s location and motion.
For example, head and neck tumors typically shrink and change shape slowly as they respond to therapy, but usually remain in a stable position relative to surrounding tissues. In such cases, once- or twice-weekly adaption is sufficient to maintain optimal dosing and coverage.1 In contrast, cervical tumors often shift in shape and position due to variations in bladder filling from one treatment to the next. These changes can be addressed with daily adaption, ensuring optimal dosing and protection of surrounding organs based on the patient’s anatomy at the time of treatment.
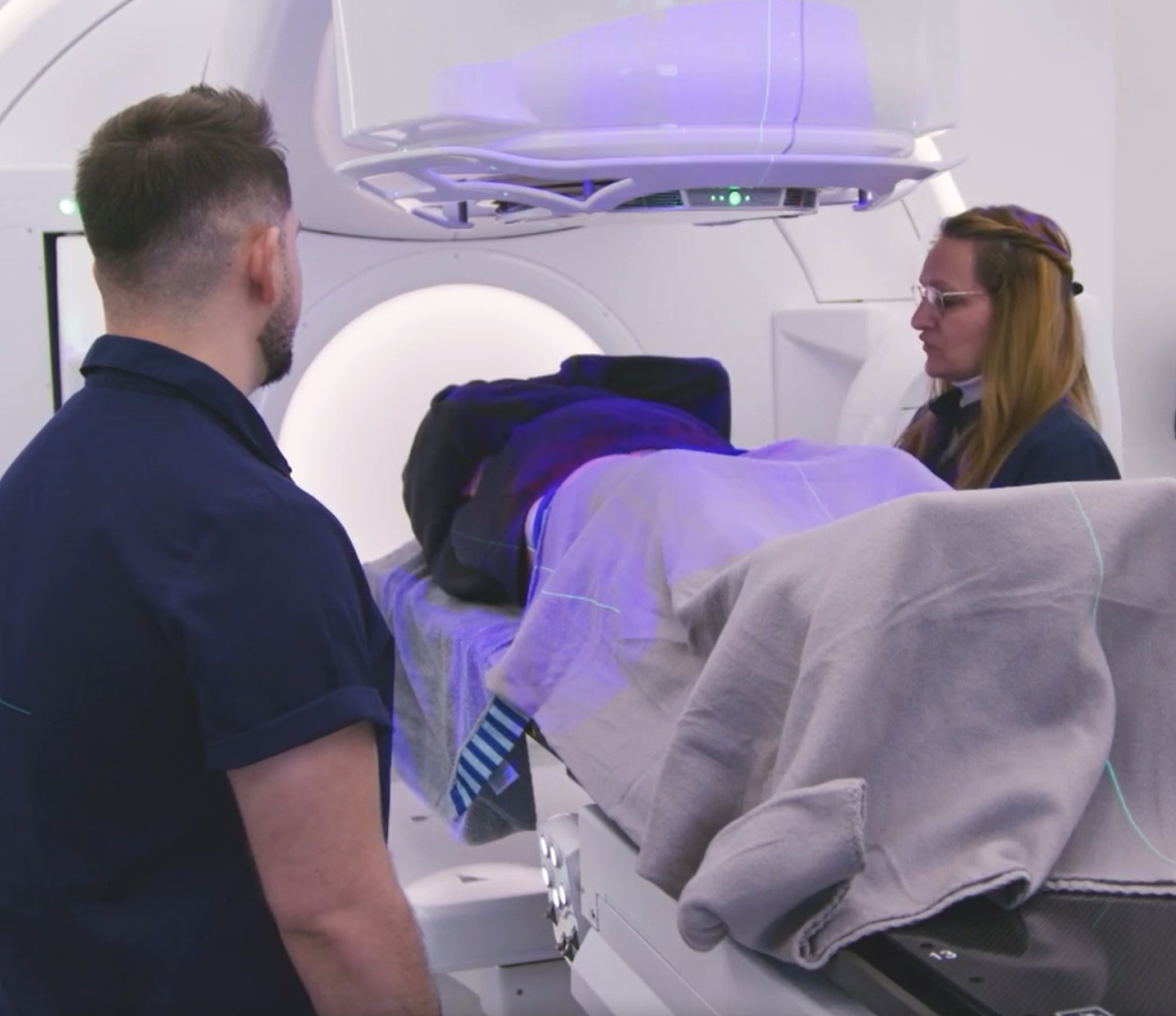
The radiotherapy team can implement Adaptive Radiotherapy using images taken while the patient is on the treatment machine (Online Adaptive Radiotherapy) or from separate imaging sessions such as CT simulation (Offline Adaptive Radiotherapy). Offline Adaptive Radiotherapy is typically performed between treatment sessions and, because it does not require the patient to be on the treatment couch, offers greater flexibility in imaging. This approach is often beneficial for clinics where advanced imaging is not co-located with the treatment machine and is most effective in adapting to systematic variations that occur gradually over time.2
Compare Imaging TechnologiesThe Case for Adaptive Radiotherapy
How global experts are calling for adaptive to become the new standard of care.
Radiotherapy is indispensable. Adaptive radiotherapy represents a transformative leap — treatments tailored in real time, maximizing tumor control while sparing healthy tissue.
From Innovation to Impact
Radiotherapy delivers a highly individualized form of cancer care by tailoring treatment schedules to tumor type, stage, and location, supported by multiple technologies. It can be used to cure or shrink tumors, prevent recurrence, manage relapsed cancers, or relieve symptoms in advanced disease. With the precision of modern technologies, radiotherapy has become the backbone of curative care for many cancers.
Radiotherapy’s versatility is a major reason it is delivered to more than half of all cancer patients worldwide. It can be used alone or in combination with other therapies, including surgery, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy. It may be delivered before surgery to reduce tumor size (neoadjuvant therapy) or after surgery to eliminate residual disease (adjuvant therapy). ChemoRT, which combines radiation with chemotherapy, is frequently deployed in locally advanced cancers to improve outcomes. Recent studies also suggest synergies between radiotherapy and immunotherapy, potentially enhancing tumor death and reducing the risk of recurrence.
Treatment planning defines not only the target volume, but also the dose and fractionation strategy. Approaches such as Intensity Modulated RT (IMRT), stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), and stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) allow higher doses per fraction with minimal exposure to surrounding tissues. Such breakthroughs enable hypofractionation treatment schedules in which the total prescribed dose is delivered over fewer treatment sessions compared with conventional radiotherapy. This reduces the total number of treatment sessions, which lessens patient burden, improves quality of life, and increases treatment efficiency and capacity.
Propelled by these advancements, Adaptive Radiotherapy is enabling radiation oncologists to deliver a more personalized, precise, and patient-centered standard of care.
Explore ART BenefitsReady to Get Started?
Contact usReferences
- Cai, Beiyi, et al. “Current Status and Future Directions of Online Adaptive Radiation Therapy.” Frontiers in Oncology, vol. 11, 2021, doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.770382.
- Green OL, Henke LE, Hugo GD. Practical Clinical Workflows for Online and Offline Adaptive Radiation Therapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2019 Jul;29(3):219-227. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2019.02.004. PMID: 31027639; PMCID: PMC6487881[SM1] [SHS2]